Thinking about minting your first NFT with Swappable? Here’s a 101 intro to NFTs for the crypto curious.
What is an NFT?
NFT stands for “Non-Fungible Token.” Non-Fungible means that the token is unique. Some NFTs have become very valuable because the owner is the only person who owns that particular NFT. Often, even if an NFT is part of a collection, each NFT within it has different characteristics that set it apart.
An NFT is a digital asset representing ownership of an object, such as a piece of art or music. NFTs are, as we already mentioned, one of a kind or one of a limited run. NFTs represent ownership of unique items. They have contributed to the livelihoods of digital artists by enabling them to sell their digital art more easily. People usually buy NFTs on an NFT marketplace hosted on a blockchain such as the Ethereum blockchain.
Tokenizing real-world assets and turning them into NFTs makes buying, selling, and trading them more efficient. Each NFT contains a unique, non-transferable identity to distinguish it from others.
NFTs not only help sell art and music, and they can also facilitate Private Equity transactions and Real Estate deals.
Why are NFTs valuable?
NFTs are valuable because they verify the authenticity of unique digital assets. Vincent Van Gogh’s paintings are non-fungible because there is only one original, and people can make prints or copies of them, but only one true original exists.
NFTs have this same quality in a digital form. With NFTs, the buyer owns a token that proves they own the original work.
Some NFTs have features to expand their purpose over time or provide utility to holders.
Since the blockchain is public, it’s also possible to send additional items to every collection owner. Public, open-source contracts provide additional value beyond simple ownership, and they give the creators a way to build a dedicated community around their brand.
Some projects build ecosystems around their NFTs where holders of an NFT from a specific NFT series gain access to additional products, activities, and experiences. The revenue goes back into the brand, making the projects more ambitious and driving up the price of the NFTs in the process.
What are gas fees?
Gas fees are payments that users must make to offset the computing energy required to process and validate transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. Your car requires gas to work, and the Ethereum blockchain requires “gas” in the form of fees to process transactions.
After payment, gas fees reward Ethereum miners who perform the work associated with processing and validating transactions on the network. If the gas price is too low, miners can ignore the request.
Gas prices fluctuate based on the supply and demand of processing power. If there is a high demand for processing power due to high transaction volume and a low supply of processing power, gas fees will increase.
What is minting?
Minting an NFT is the process of publishing the token on a blockchain so that someone can purchase the NFT. Essentially, it’s turning a collectible into a uniquely tradable token that can be bought and sold on a blockchain. Many popular NFT marketplaces make it quite simple to mint NFTs and sell them on their platforms. Minting an NFT requires you to have a crypto wallet first before getting started.
Selling an NFT requires computing, requiring you to pay a gas fee. After the minting process completes, you will need to have some crypto in your wallet to sell it to a buyer.
What are some examples of Layer 2 blockchains?
Layer 2 blockchains are essential because they increase transaction speed and reduce fees. Some examples of Ethereum layer two blockchains are Polygon and Polkadot. A popular Bitcoin Layer 2 blockchain is the Lightning Network. However, these are not the only Layer 2 blockchain solutions. Here is a list of some other Layer 2 projects. To be considered a Layer 2, a project must be a secondary framework built on an already existing blockchain system.
What is secondary trading?
Secondary trading is trading on the secondary market. The primary market is where cryptocurrencies are made available to the public for the first time, so investors buy them from the project or company issuing them. In the secondary market, these cryptocurrencies already exist and are traded between different investors.
Unless you bought cryptocurrencies or NFTs directly from the crypto project issuing them in an ICO, IDO, or INO, you are likely buying them from other investors on the secondary market. Different investors and crypto/NFT enthusiasts then trade the assets.
What is a smart contract?

A smart contract establishes the terms of an agreement between people, just like any contract. A smart contract differs from other contracts in that the terms of the agreement between the buyer and seller are in lines of code.
Contract terms execute automatically based on code that runs on-chain. There is no business or intermediary overseeing the transaction, and Blockchain-enabled code allows transactions to remain decentralized since the transaction terms don’t require an intermediary to execute.
Smart contracts are a vital component of decentralized apps or “dapps.” Apps focused on decentralized finance via smart contracts allow cryptocurrency holders to complete complex financial transactions without a bank or other financial institution overseeing the trade and taking a cut of the profits.
Many popular platforms use smart contracts, but one of the most popular ones today is Uniswap, a decentralized crypto trading protocol.
Smart contracts also exist in NFT transactions, just as in other crypto transactions.
What is MetaMask?
MetaMask is a popular crypto wallet and gateway to blockchain applications. It is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets and is used to interact with the Ethereum blockchain. Since many other crypto projects run on the Ethereum blockchain, it has become one of the most widely used crypto wallets globally, with 21 million+ users worldwide.
Consensys, a popular project that builds blockchain products to be used to interact with the Ethereum blockchain, initially developed MetaMask.
What is a crypto exchange?

A crypto exchange is a digital platform or marketplace where you can buy and trade cryptocurrencies. If you decide that you want to buy crypto, you will need to create an account on a crypto trading platform like a crypto exchange to exchange your fiat currency for digital assets.
Not all crypto exchanges offer fiat to crypto onramp. Centralized exchanges, or CEXs, still maintain some degree of centralization, but they offer a relatively simple and hassle-free way to buy and trade crypto. Decentralized exchanges, or DEXs, are much more decentralized and can be complicated since the exchange does not directly assist with transactions.
Some of the popular crypto exchanges that you can still use today started during the early days when fewer people were involved in the crypto space.
What happens when you buy an NFT?
When you buy an NFT, you get to say that you own the original copy of a digital file, and the NFT provides digital proof of ownership. Essentially, purchasing an NFT executes a transaction that now identifies you as an owner of a unique digital asset.
The process is similar to someone purchasing an original painting, but this form of ownership is digital. NFTs come with a digital signature proving that you own them.
If the NFT is rare or from a trendy collection, it will likely grow in value and become valuable. When you purchase an NFT, you are also investing in that project.
When you purchase an NFT, ownership transfers from the creator of the NFT or its previous owner to you in exchange for your payment for it in cryptocurrency.
What are some examples of NFT projects?
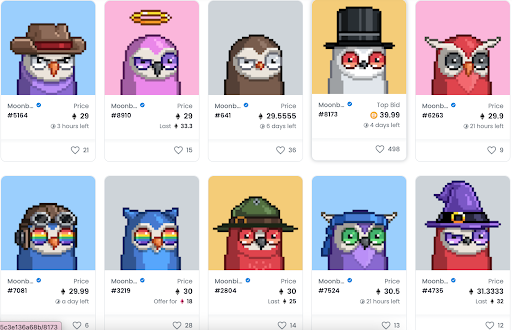
Moonbirds are one of the top 10 NFT projects globally by floor price! Moonbirds are a collection of 10,000 PFPs that feature rarity-powered traits. Moonbirds unlock club membership and other benefits the longer you hold them. They are one of the most popular NFT projects right now.
Alien Frens is another popular limited NFT collection. Your Alien Fren grants you access to an exclusive lifelong friendship. There are 10,000 NFTs in the collection.
Art Blocks is an NFT project on Ethereum that generates original digital artwork via an algorithm.
Gutter Cats are a unique NFT collection based on a futuristic world where cats have taken over, and one city is inhabited by a group of cats known as the Gutter Cats.
There are thousands of NFT communities boasting different benefits and utilities in the real world and the metaverse. Even with fantastic utility, style and vibes are a critical part of the success of any NFT project. The best idea in the world will get overlooked if no one wants to be a part of your club.
Buy, sell, trade, chat, hang out. And as always, DYOR.